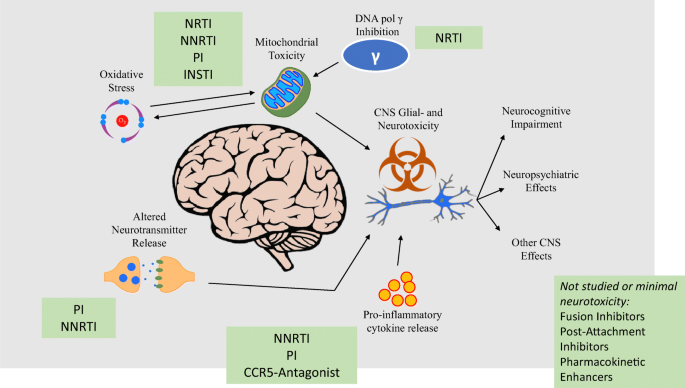
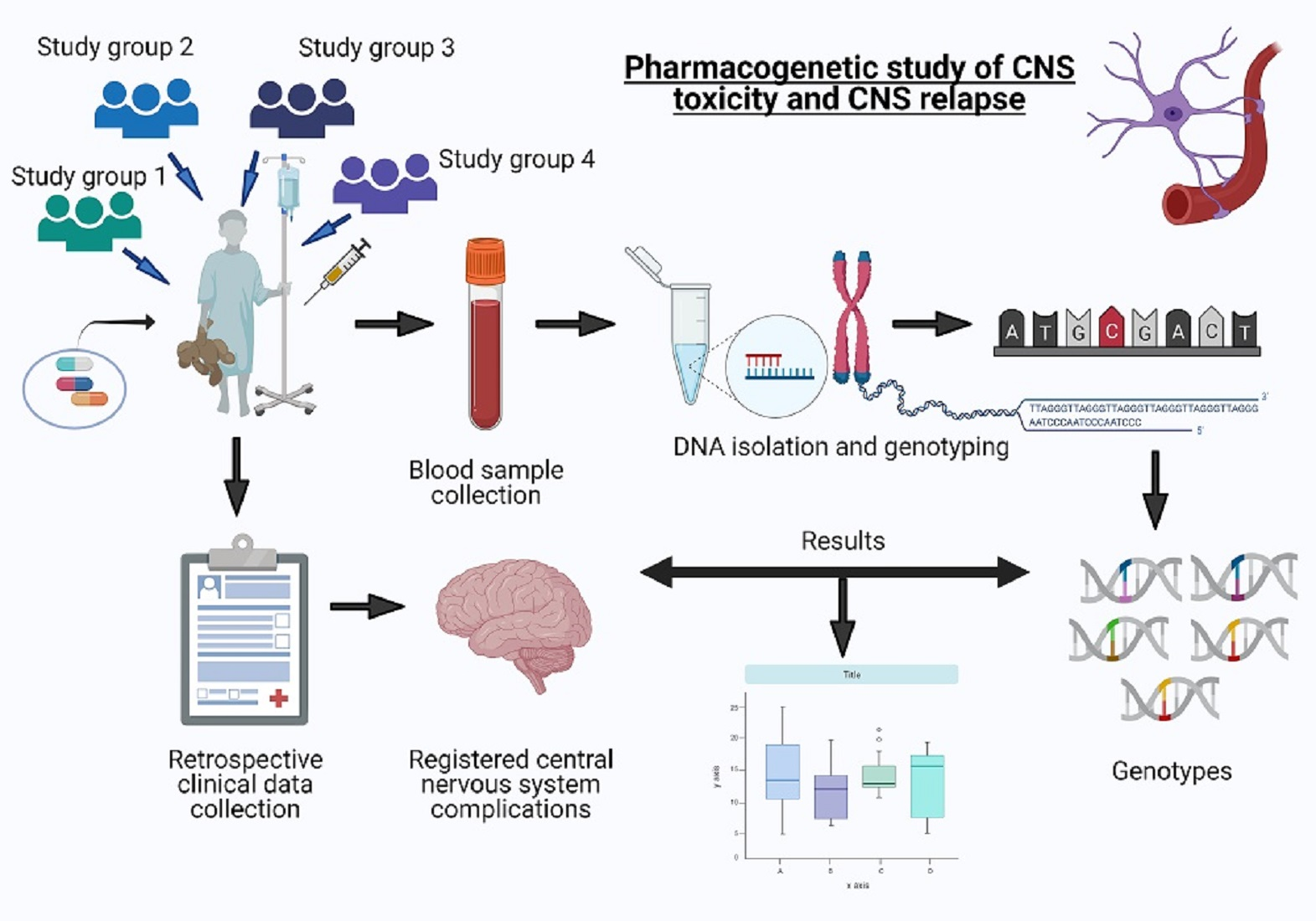
Central Nervous System Toxicity
Central nervous system toxicity. Central nervous system toxicity. Although there has been a significant interest in the development and validation of biomarkers the area of central nervous system CNS toxicology has received only limited attention particularly with regard to biomarkers of effects and of susceptibility. Visual deficits were the most common presenting symptom and developed eventually in most cases.
The means of exposure may be intentional or unintended. Central nervous system toxicity of metallic nanoparticles Xiaoli Feng1 Aijie Chen1 Yanli Zhang1 Jianfeng Wang2 Longquan Shao1 Limin Wei2 1Nanfang Hospital Southern Medical University Guangzhou Peoples Republic of China. The CNS affects are slowing or incompletely reversible.
CNS toxicity was dose-related since patients treated for 12 consecutive doses of 45 gm2 had significantly greater CNS toxicity than 12 consecutive doses at 3 gm2 P less than 004. All authors contributed to concept and design. However it has been rarely reported that mefenamic acid can induce central nervous system toxicity both in toxic doses and therapeutic usage.
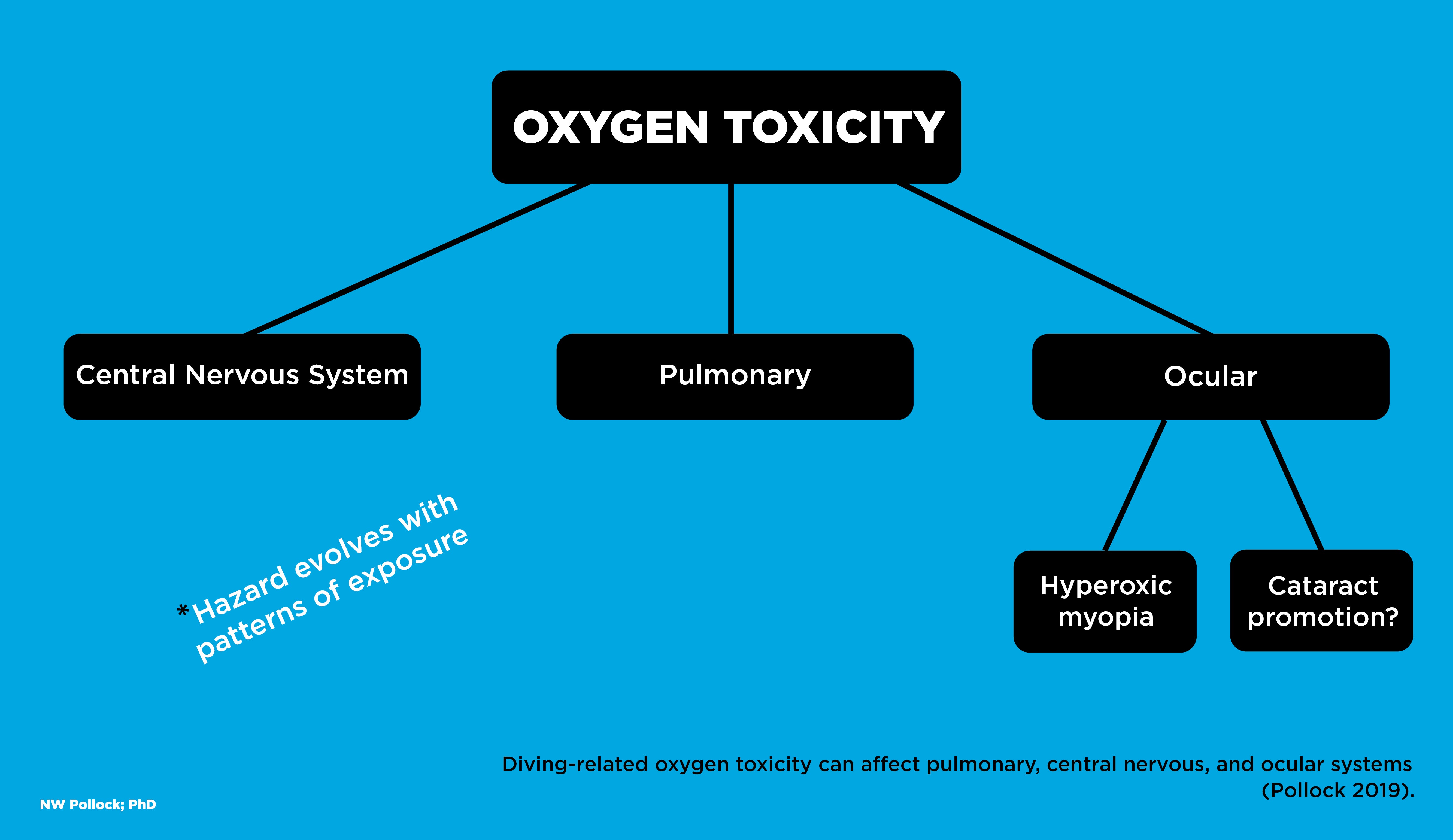
Metronidazole can rarely cause central nervous system toxicity. It occurs when exposure to a substance specifically a neurotoxin or neurotoxicant alters the normal activity of the nervous system in such a way as to cause permanent or reversible damage to nervous tissue. CNS toxicity as described originally by Bert occurred at oxygen pressures of 3 ATA.
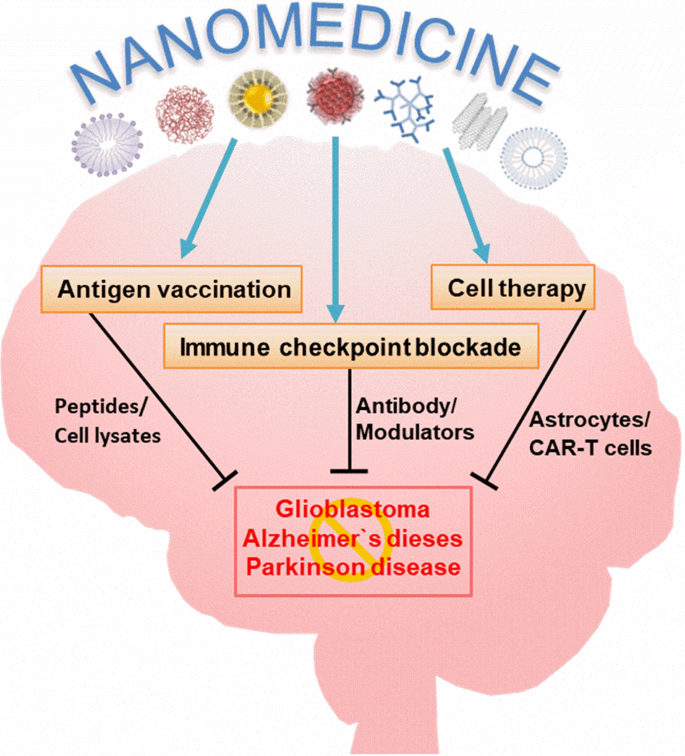
It does not seem to be a dose- or duration-related phenomenon. High intravenous doses of methylthioninium chloride methylene blue should be avoided for patients being treated with serotonergic antidepressants eg SSRIs clomipramine and venlafaxine. Nanomaterials NMs are increasingly used.
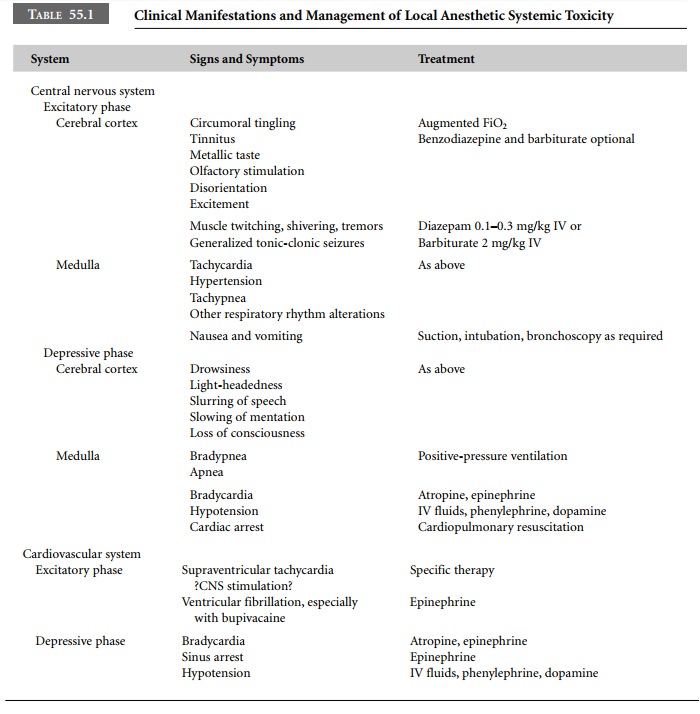
Central nervous system toxicity is biphasic initially excitatory with lowering of seizure threshold. Central nervous system toxicity is unusual with vinca alkaloids because they do not readily cross the. Sources of exposure may be medicinal recreational environmental or occupational.
Systemic cytarabine doses less than 54 gm2 can be administered with minimal CNS side-effects. We report a case of a 27-year-old female who presented to the emergency.
Metronidazole can rarely cause central nervous system toxicity.
Ilkhchoui prepared the manuscript as well. Mefenamic acid is a fenamate nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory NSAI drug which is used for several years for pain management. High intravenous doses of methylthioninium chloride methylene blue should be avoided for patients being treated with serotonergic antidepressants eg SSRIs clomipramine and venlafaxine. Deterioration of mental status and progressive encephalopathy were also observed. Central nervous system toxicity. It does not seem to be a dose- or duration-related phenomenon. The CNS affects are slowing or incompletely reversible. Although there has been a significant interest in the development and validation of biomarkers the area of central nervous system CNS toxicology has received only limited attention particularly with regard to biomarkers of effects and of susceptibility. Central nervous system toxicity is biphasic initially excitatory with lowering of seizure threshold.
2School and Hospital of Stomatology Wenzhou Medical University Wenzhou Peoples Republic of China Abstract. Sci Vol28 No4 July 2015 pp1417-1423 neurological finding in chronic toxicity. Brain as a target organ 1418 Pak. The means of exposure may be intentional or unintended. Central nervous system toxicity of metallic nanoparticles Xiaoli Feng1 Aijie Chen1 Yanli Zhang1 Jianfeng Wang2 Longquan Shao1 Limin Wei2 1Nanfang Hospital Southern Medical University Guangzhou Peoples Republic of China. Central nervous system toxicity caused by xenobiotic exposure is a common reason for presentation to the emergency department. Sources of exposure may be medicinal recreational environmental or occupational.





































Post a Comment for "Central Nervous System Toxicity"